Transitioning Master Data Management to Shared Services/GBS
Introduction
A recent Peeriosity-100 Peercast featured Master Data Management experts from three member companies. The Peercast format was a panel discussion on master data management approaches across different companies – Co A, Co B, and Co C. The panelists shared insights into their respective organizations’ master data management teams, scope, processes, and the impacts of formalizing these efforts. Key points discussed include centralization and standardization of master data processes, leveraging technology for automation and governance, fraud prevention measures, and the importance of data quality for enabling strategic analytics and AI initiatives. The discussion highlights the value of having dedicated master data organizations for improving efficiency, consistency, and data accuracy across the enterprise.
Company Experiences
Co A’s Financial Master Data Organization
The Company A presenters explained that their organization focuses on financial master data services, covering 10 critical domains such as accounts, company codes, cost centers, and geography. Established in 2017 as part of the S/4HANA implementation, the team of 23 business members supports projects and operations. They leverage technology like SAP Fiori and workflow functionality for automation and governance. The team also uses a stewardship tool to track measures like accuracy and timeliness across different systems.
Co B’s Data Management Organization
The presenter from Company B shared that their data management organization (DMO) supports domains like product, vendor, customer, and pricing data. With a team of 25 members, they leverage an outsourcing model for operational execution. The DMO has two branches – one focused on operations and standard requests, and the other on M&A integrations and data cleansing. They recently deployed a workflow tool for vendor management, enabling self-service and fraud prevention through banking validation. The DMO also aims to enable strategic analytics and AI initiatives by ensuring data quality.
Co C’s Global Shared Services and Master Data
The presenter from Company C’s Global Shared Services (GSS) organization explains that they formed a dedicated master data workstream about a year ago. Currently, they own customer and vendor master data processes, with a team of 20 people in India managing operational requests. They have Global Process Managers for customer, vendor, and material master data. The goal is to centralize and standardize processes, identifying opportunities for improvement and value creation through process analysis and automation.
Impact of Master Data Management Approaches
The panelists discussed the impacts of their master data management approaches. For Co A, it has enabled quality, capability, and efficiency improvements through centralized processes, automation, and governance. Co B highlights fraud prevention benefits from their vendor management workflow and banking validation tools. They also aim to enable strategic analytics and AI through data quality. Co C is at the start of realizing value, identifying opportunities for process streamlining, standardization, and waste reduction through centralized ownership and analysis.
Expanding Scope and Change Management
The discussion turned to expanding the scope of master data management and the change management process involved. Co A has added new dimensions over time, assessing where centralized ownership can add value. Co B and Co C are actively exploring opportunities to expand their services to other domains like materials and sales hierarchies, partnering with business stakeholders to demonstrate value and earn trust. Change management is highlighted as crucial, with dedicated teams facilitating transitions and optimizing the process.
Key Points to Consider:
- Explore opportunities to expand the scope of master data management services to other domains like materials, sales hierarchies, and employee data, by partnering with business stakeholders and demonstrating the value proposition.
- Implement robust change management processes and dedicated teams to facilitate the transition of master data ownership and optimize the process based on learnings.
- Leverage technology solutions like workflow tools, banking validation plugins, and data stewardship platforms to automate processes, enhance governance, and ensure data quality.
- Continuously assess the impact of master data management approaches, focusing on metrics like efficiency, consistency, fraud prevention, and enabling strategic analytics and AI initiatives.
- Foster collaboration and knowledge-sharing among master data organizations across different companies to benchmark best practices and learn from each other’s experiences.
Polling Results Review
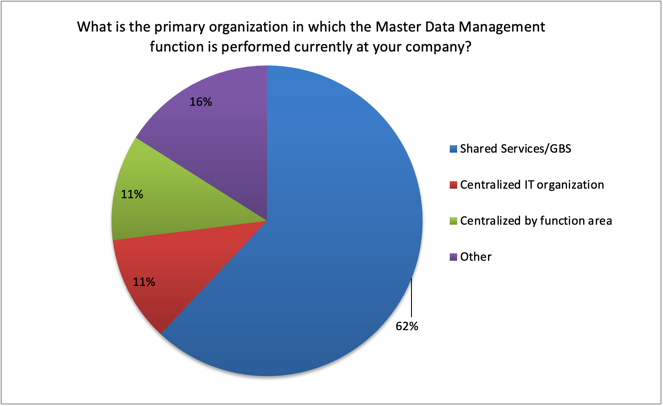
Peeriosity-100 Polling was used to better understand the status of member companies transitioning Master Data Management to Shared Services/GBS. The first polling question asked about the primary organization where Master Data Management is performed. Most companies, at 62%, the primary organization is Shared Services/GBS. The balance of 38% of the companies either primarily centralize by functional area, within IT, or following some other method. Here are the details:
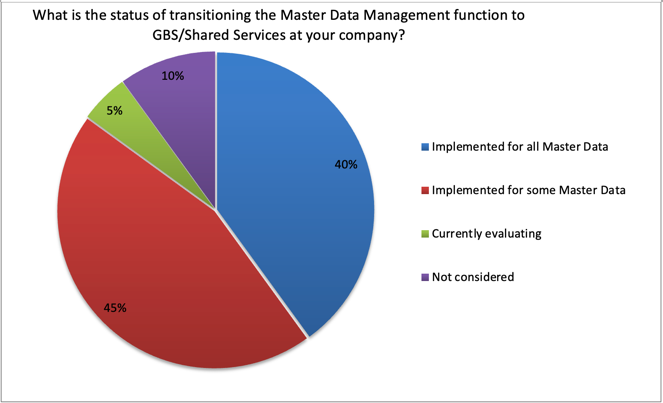
The second poll question asked about the status of transitioning Master Data Management to Shared Services/GBS for all types of Master Data. 40% of member companies have implemented for all types of Master Data, and 45% report that they have implemented for some types of Master Data. The balance of 15% are either evaluating or they have not considered having Master Data Management in Shared Services/GBS.
Here are some comments from responding companies:
- We are early in our journey, brought in ~90% for Customer and Vendor data, have not yet started on Material or other domains.
- We have 2 master data teams essentially, one is within IT for SAP HCM related master data updates, and the other is a centralized business team to support all other functional areas master data updates for SAP ECC.
- Some items are centralized (final approvals, banking info, etc) and most items are decentralized to the business units. As we move to a new ERP, we are working to centralize all pieces of business partner data for consistency and accuracy.
- GBS currently maintains Material Master, Customer Master, Vendor Master and pricing master data. We are expanding into other domains shortly.
- Supplier admin in procurement and employee data in HCM are the two specific ones I can validate and both in Oracle.
- GBS owns Vendor/Customer master data. And we will transition Material Master Data (Raw, pack, Intermediate, FP, BOMs, recipes) in 2025.
- Several areas within GBS; but some master data (e.g., lane rates for freight) remain with other organizations.
- Most master data (customer, vendor, material, GL, cost center) is updated by shared services. Some pricing data and other data not centrally managed by same team.
- It is decentralized. Some sub process is central at SS while a lot of it is still in business.
- Approx 90% in scope of our SSC.
Closing Summary
Having high quality Master Data is critical for the smooth operation of any business. Traditionally, Master Data was decentralized by business or geography and managed by the function that was most involved in the process of entering or maintaining the data. The common result was to have Master Data in different databases with inconsistencies and errors, because of inefficient and error prone processes for entering and maintaining the data. For some, consistency across business and/or geographies wasn’t even part of the strategy.
With the introduction of Shared Services/GBS organizations that have a customer focus and expertise in quality management tools and techniques, and expertise in the latest tools and technologies, Shared Services/GBS is perfectly positioned to manage Master Data processes. As a result, instead of Master Data being a secondary responsibility of a functional area, Master Data becomes a primary responsibility as a Center of Excellence within the overall umbrella of Shared Services/GBS.
How does you company Manage Master Data processes? What parts are in Shared Services/GBS, and how do you ensure quality and accuracy?
Who are your peers and how are you collaborating with them?
________________________________________________________________
Peercasts are private, professionally facilitated webcasts that feature leading member company experiences on specific topics as a catalyst for broader discussion. Access is available exclusively to Peeriosity-100 member company employees, with consultants or vendors prohibited from attending or accessing discussion content. Members can see who is registered to attend in advance, with discussion recordings, supporting polls, and presentation materials online and available whenever convenient for the member. Using Peeriosity-100’s integrated email system, Peer Mail, attendees can easily communicate at any time with other attending peers by selecting them from the list of registered attendees.
Polling is available exclusively to Peeriosity-100 member company employees, with consultants or vendors prohibited from participating or accessing content. Members have full visibility to all respondents and their comments. Using Peeriosity-100’s integrated email system, Peer Mail, members can easily communicate at any time with others who participated in Polling.

